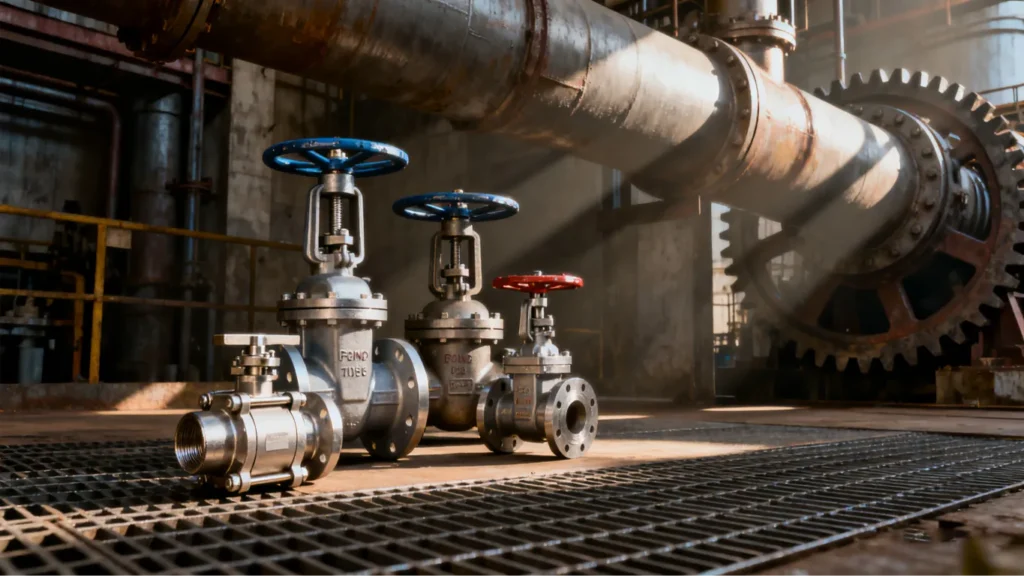
In industrial fluid transport systems, industrial valves are core control components that directly affect operational safety, efficiency, and maintenance costs. Whether it’s oil and gas pipelines, water treatment plants, or chemical processing facilities, selecting the correct valve type based on working conditions can reduce failure rates by over 60% and extend service life by 2-3 times . This guide will break down key selection factors and mainstream valve applications to help you make informed decisions.
Key Factors for Industrial Valve Selection
1. Medium Characteristics
- Corrosive media (acids, alkalis, saltwater): Prioritize corrosion-resistant valves such as lined fluorine valves or stainless steel valves.
- Media with solid particles (sludge, ore pulp): Choose full-port ball valves or gate valves with wear-resistant structures to avoid clogging .
- High-viscosity media (syrup, heavy oil): Opt for valves with low flow resistance, like gate valves or eccentric rotary valves .
- Toxic/flammable gases: Select valves with ANSI Class V+ sealing performance to ensure zero leakage .
2. Pressure and Temperature Parameters
- Low pressure (<1.6MPa): Butterfly valves or globe valves are cost-effective choices for large-caliber pipelines .
- Medium pressure (1.6-10MPa): Ball valves or gate valves meeting PN16-PN40 standards offer reliable sealing .
- High pressure (>10MPa): Industrial valves complying with API 600/609 standards, such as metal hard-seal ball valves, are essential .
- Low temperature (<-29℃): Low-temperature steel valves (304L/316L material) with special sealing gaskets prevent cold brittleness .
- High temperature (>300℃): Hard-seal gate valves or ball valves resistant to 350℃+ environments are suitable for steam pipelines .
3. Connection and Operation Methods
- Small-caliber pipelines (DN≤50): Threaded connection valves for easy installation .
- Large-caliber pipelines (DN≥300): Flanged connection or welded connection valves for stability .
- Frequent operation (≥3 times/min): Electric ball valves with 100 万 + cycle life outperform globe valves .
- Explosion-proof areas: ATEX/IECEx certified pneumatic valves with response time <0.3 seconds .
Application Scenarios of Mainstream Valve Types
| Valve Type | Core Advantages | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Ball Valve | Fast 90° opening/closing, excellent sealing | Oil and gas emergency shutoff, pharmaceutical clean systems, marine pipelines |
| Gate Valve | Low flow resistance, suitable for full open/close | Power plant steam pipelines, municipal water supply mains (DN≥100) |
| Globe Valve | Precise flow regulation | Thermal power plant steam control, laboratory sampling systems |
| Butterfly Valve | Compact design, cost-effective for large caliber | Water treatment plants, low-pressure air pipelines (DN>600) |
| Check Valve | Prevents backflow | Compressor exhaust pipelines, boiler feedwater systems |
Maintenance and Compliance Tips
- Implement predictive maintenance: Regularly inspect sealing surfaces and valve stems, especially for valves in high-temperature/pressure environments .
- Match international standards: EU markets require CE-PED certification, while US high-pressure applications need API 6D compliance .
- Spare parts preparation: Stock common components for ball valves and gate valves to reduce downtime .
Choosing the right industrial valve is not just about product parameters—it’s about aligning with your entire system’s needs. If you need customized solutions for specific industries (oil and gas, chemical, water treatment), our engineering team can provide tailored valve selections based on your medium, pressure, and temperature data.